Outsourcing is the practice of delegating specific business processes or functions to external service providers instead of handling them in-house. This strategy allows organizations to focus on their core competencies while leveraging the expertise and resources of third-party vendors. Outsourcing can encompass various areas, including manufacturing, customer service, IT services, and project management, often resulting in cost savings, increased efficiency, and access to specialized skills.
Strategic outsourcing is increasingly adopted by businesses to enhance efficiency, innovation, and scalability by leveraging external expertise and advanced technologies. This approach fosters long-term partnerships, enabling companies to focus on core functions while adapting to market changes and maintaining a competitive edge.
Are you ready to enhance the efficiency of your business? With Go Carpathian, you can outsource to Eastern Europe, South Africa, and Latin America. Schedule a call with a recruiting specialist today!
In this post, we will explore how outsourcing can affect profit margins while maintaining the quality of work. We will also compare operational costs between companies that outsource and the ones that don’t.

What is Strategic Outsourcing?
Strategic outsourcing is the practice of delegating specific business functions or processes to external providers to enhance performance, efficiency, and competitive advantage. Its significance lies in allowing companies to focus on specialized skills while leveraging specialized expertise and resources, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency, innovation, and the ability to adapt quickly to market changes.
Strategic outsourcing is prevalent across various key industries, exemplified by several notable practices. In IT, companies like Google outsource customer support and data management to specialized firms, allowing them to focus on innovation while ensuring efficient service delivery. In customer service, Alibaba outsources its support functions to manage its extensive customer base effectively, enhancing service quality and operational efficiency. In manufacturing, Apple relies on partners like Foxconn for the production of its devices, enabling the company to concentrate on design and innovation while benefiting from the manufacturers’ expertise and scale. These examples illustrate how strategic outsourcing can drive efficiency and competitive advantage in modern businesses.
Types of Outsourcing
Outsourcing is a business practice where a company hires a third party to perform tasks, handle operations, or provide services. Traditional outsourcing primarily focuses on cost reduction by contracting out non-core functions, whereas strategic outsourcing aims to build collaborative, value-added partnerships that enhance innovation, efficiency, and overall competitive advantage.
Nearshoring and offshoring are both types of outsourcing, but they differ geographically. Nearshoring involves outsourcing to a neighboring country or region, while offshoring means outsourcing to a more distant country. Offshoring is typically cheaper due to lower labor costs in distant regions, but it can present challenges related to communication, time zone differences, and cultural barriers.
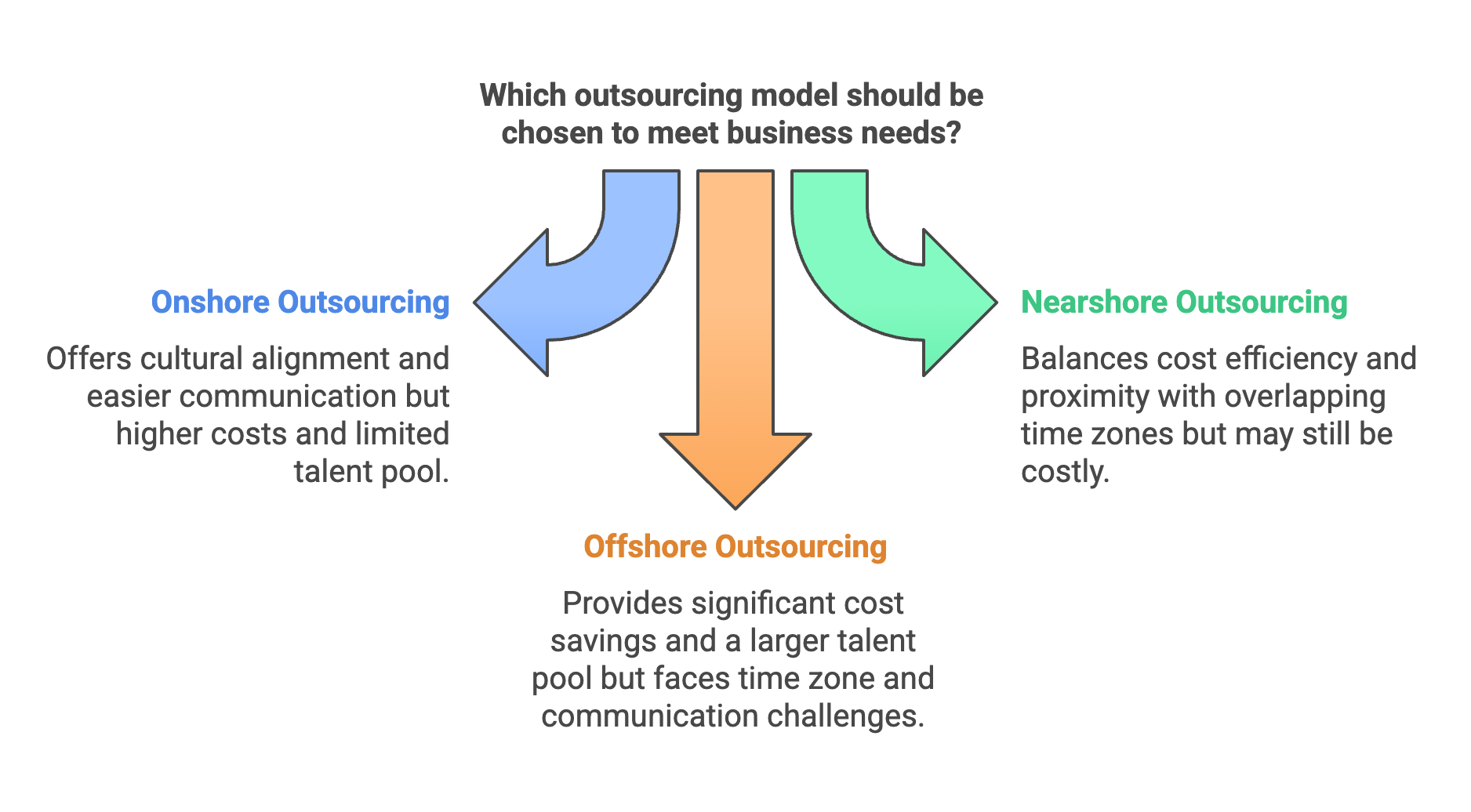
Outsourcing models have evolved to meet the diverse needs of modern businesses, with three primary types: onshore, nearshore, and offshore outsourcing.
Onshore Outsourcing involves contracting services from companies within the same country. This model offers benefits such as cultural alignment, easier communication, and compliance with local regulations. However, it often comes with higher labor costs and a limited talent pool.
Nearshore Outsourcing refers to partnering with service providers in neighboring countries. This model strikes a balance between cost efficiency and proximity, allowing for overlapping time zones that facilitate real-time collaboration. While it can reduce some challenges associated with cultural differences, it may still present higher costs compared to offshore options.
Offshore Outsourcing involves hiring third-party contractors in distant countries, typically to leverage lower labor costs and access a larger talent pool. This model is popular for its significant cost reductions but can present challenges related to time zone differences and potential communication barriers.
The Impact of Outsourcing on Business Operations & Efficiency
Outsourcing significantly impacts business operations by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and allowing companies to focus on expert knowledge. By delegating non-core tasks to specialized providers, businesses can streamline processes, improve productivity, and accelerate innovation. Outsourcing also provides access to industry best practices and expertise that may not be available internally, leading to better quality control and faster time-to-market for products or services. This strategic approach enables businesses to scale operations more effectively while maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Cost Saving and Cost Comparison
For a 7-figure marketing business, comparing the costs between outsourcing and in-house operations involves several key factors. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Operational Costs Comparison
There is a significant difference between in-house operations costs and outsourced operations costs. To help business owners understand these costs better, we created an in-depth analysis:
In-House Operations
In-house operations include specific types of cost that can be divided into direct and indirect costs.
Direct Costs:
Salaries and Benefits: Employee salaries, health insurance, retirement plans, and other benefits can be substantial. For a marketing team of ten professionals in the U.S., this could range from $500,000 to over $1 million annually.
Office Space: Renting office space for the team adds significant overhead costs. In major cities like New York or Los Angeles, this could exceed $100,000 per year.
Equipment and Technology: Maintaining up-to-date software tools and hardware for the team is another expense.
Indirect Costs:
Training and Development: Continuous training to keep skills updated can add thousands of dollars annually.
Management Overhead: Additional management layers are needed to oversee internal teams.
Outsourced Operations
When it comes to outsourcing, the costs can also be divided into direct and indirect costs, but the main difference is that outsourcing costs are much lower compared to in-house costs.
Direct Costs:
Service Fees: Outsourcing partners typically charge fixed fees or hourly rates. For example, outsourcing marketing services might cost between $20,000 to $50,000 per month depending on scope.
Indirect Costs:
While there are fewer indirect costs compared to in-house operations (e.g., no need for office space), businesses must still consider management time spent overseeing outsourced relationships.
Cost Reduction Analysis
Outsourcing can offer significant cost reductions by reducing overhead expenses such as office space rental and equipment maintenance. Additionally, it allows businesses to avoid upfront investments in hiring and training new employees. However, indirect costs like communication overheads should be factored into overall expenses
Strategic Considerations
For a high-revenue business like a 7-figure marketing company:
Outsourcing non-core functions (e.g., IT support) can free up resources for strategic activities while maintaining efficiency.
Nearshore or offshore outsourcing may provide additional reductions due to lower labor costs but requires careful consideration of cultural alignment and communication challenges.
The choice between insourcing vs outsourcing depends on whether specialized expertise is readily available internally or if external providers offer better value through economies of scale.
Ultimately, while both models have their advantages depending on specific needs (control vs flexibility), outsourcing often provides more predictable monthly expenses without long-term commitments associated with full-time employees.
Example Cost Structure
Category | In-House Operations | Outsourced Operations |
Salaries & Benefits | High ($500K-$1M/year) | Included in Service Fees |
Office Space | Significant ($100K/year) | Minimal |
Equipment & Technology | Ongoing Expenses | Often Included by Provider |
Training & Development | Continuous Expenses | Limited |
Management Overhead | Higher | Lower |
This comparison highlights how outsourcing can streamline operational budgets by eliminating certain fixed costs associated with maintaining an internal workforce.
How Offshoring Changes Profit Margins
Outsourcing can improve profit margins by enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. By delegating non-core functions to specialized providers, businesses can streamline operations, lower labor and infrastructure expenses, and access advanced technologies without significant upfront investments. This strategic approach allows companies to focus on expert knowledge while optimizing resources, leading to increased productivity and reduced overhead costs that directly contribute to higher profit margins.
Here are several case studies of businesses that have successfully increased their profitability through outsourcing:
Strategy: Outsourced customer support and IT services to reduce costs and leverage global talent.
Outcome: Enhanced efficiency, improved service quality, and maintained focus on innovation.
Strategy: Outsourced software development to accelerate product launch and reduce development costs.
Outcome: Rapid market entry, cost reductions, and enhanced core business focus.
Strategy: Outsourced customer support operations to maintain a lean internal team while ensuring high-quality user support.
Outcome: Operational efficiency improvements, cost reductions, and effective multilingual support for its global user base.
Strategy: Outsourced website development and maintenance to international firms during its early years.
Outcome: Focused on building its business model while expanding market presence effectively.

How to Maintaining Quality of Work While Outsourcing
One of the biggest fears associated with outsourcing is the potential decline in quality, as businesses worry that external providers may not meet their standards. Concerns about language proficiency, particularly English fluency, can also arise, leading to miscommunication and misunderstandings. Additionally, cultural fit can pose challenges, as differences in work practices and values may affect collaboration. However, these fears can be mitigated through thorough vetting of outsourcing partners, clear communication protocols, and establishing strong relationships to ensure alignment in quality and expectations.
To ensure quality standards are met by outsourcing partners, businesses should clearly define and communicate their expectations, establish measurable quality criteria, and implement regular audits and reviews to monitor performance. Additionally, fostering a collaborative relationship, leveraging technology for real-time monitoring, and selecting partners with relevant industry experience and certifications are crucial for maintaining high-quality standards in outsourcing arrangements.
With Go Carpathian, business owners can be sure they will only be connected with pre-vetted candidates who are great cultural fits and possess specific professional qualities.
How to Hire Offshore?
To hire the right talent offshore, businesses should start by assessing their business goals, identifying skill gaps, and crafting clear job descriptions that align with their needs. Conducting structured interviews, using technical assessments, and implementing a strong onboarding process helps ensure a good cultural and technical fit, leading to long-term retention and business success.
Key Factors for Successful Outsourcing
These factors help mitigate risks associated with offshore outsourcing and ensure successful project outcomes:
Vendor Selection: Choosing the right vendor involves evaluating factors such as trust, efficient communication, cultural understanding, and the quality of offshore staff. It’s crucial to assess the vendor’s expertise, industry knowledge, and ability to meet project requirements.
Contract Management: Effective contract management requires defining clear project goals, establishing a partnership-like relationship, and ensuring contract flexibility. This includes setting up a comprehensive business case and defining project standards to ensure both parties are aligned.
Ongoing Oversight: Continuous communication flow, regular face-to-face meetings, and continuous control of project results are essential for successful project execution. Additionally, ensuring a bilateral know-how transfer and maintaining a high-quality IT infrastructure supports ongoing success.
Should you hire an Outsourcing Partner?
Choosing the right outsourcing partner is crucial for maintaining quality when hiring offshore because it ensures alignment with business objectives, expertise, and reliability. A well-chosen partner can drive innovation, improve service quality, and deliver cost savings, while a poor choice can lead to inefficiencies, communication challenges, and missed business goals. Key considerations include evaluating the partner’s track record, expertise, cultural fit, communication skills, and reputation through reviews and testimonials. Conducting trial projects can also help assess their work quality and collaboration style before committing to a full partnership. By selecting a suitable partner, businesses can leverage specialized talent, streamline operations, and enhance productivity while maintaining high-quality standards.
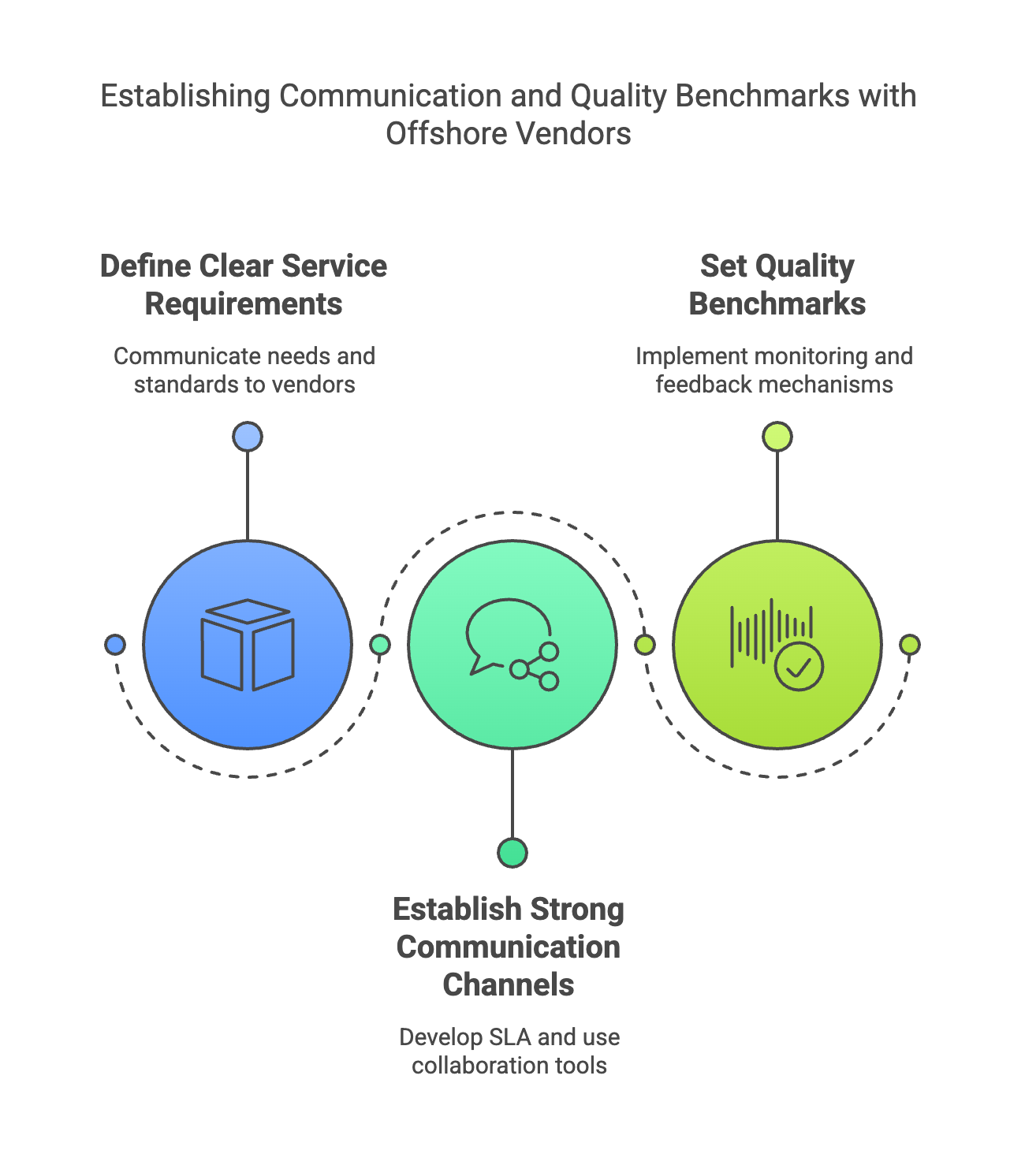
To establish clear communication and quality benchmarks with offshore vendors, follow these steps:
Define Clear Service Requirements: Communicate your needs, expectations, and standards to ensure the vendor understands your goals and can offer tailored solutions.
Establish Strong Communication Channels: Develop a detailed Service Level Agreement (SLA) and use collaboration tools to facilitate clear communication. Designate specific contact points and schedule overlap periods to minimize time zone challenges.
Set Quality Benchmarks: Implement regular monitoring and feedback mechanisms to ensure that geographically dispersed teams maintain high standards. This includes setting measurable performance goals and conducting regular reviews to address any issues promptly.
Cost Analysis for Outsourcing Functions
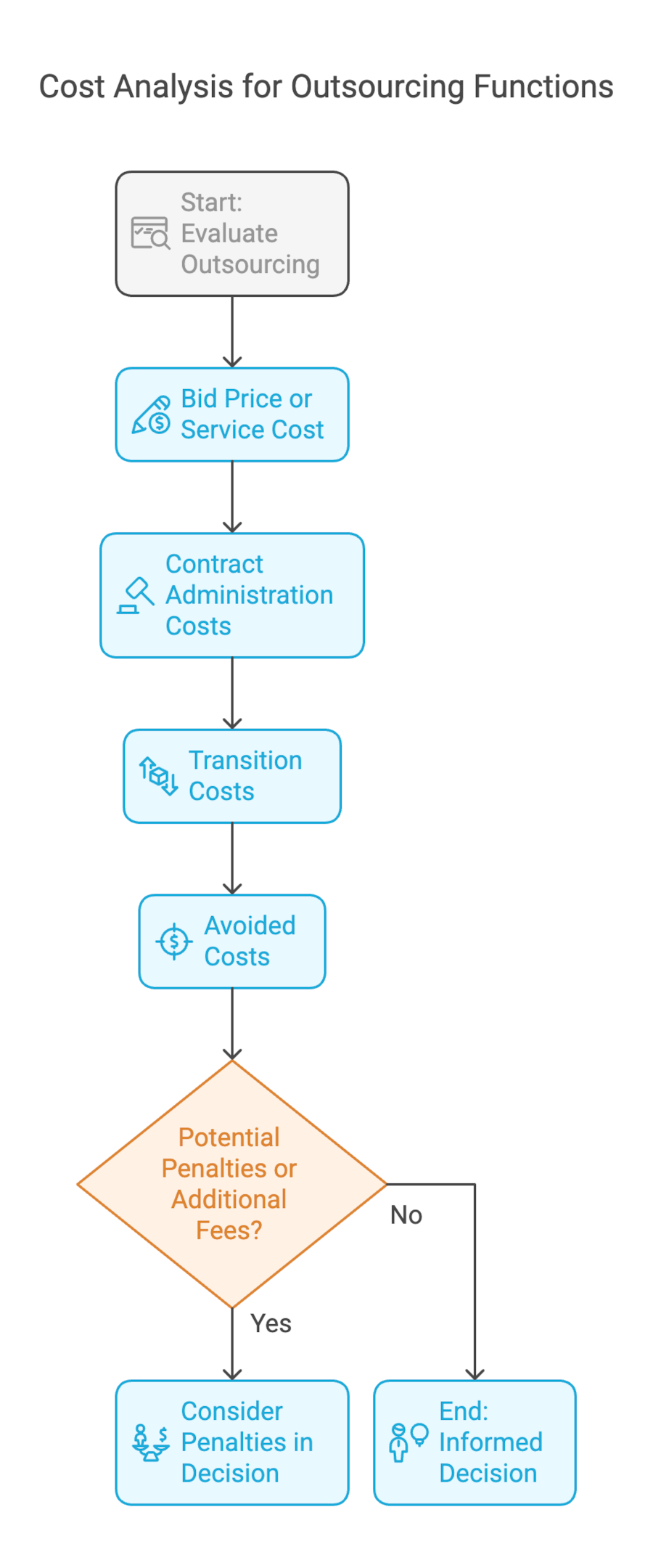
By understanding the cost components, businesses can effectively evaluate the financial implications of outsourcing specific functions and make informed decisions about whether outsourcing aligns with their budget and operational goals. Here are the key cost components for outsourcing:
Bid Price or Service Cost:
This includes the hourly rate, fixed fees, or project-based costs charged by the outsourcing provider for services such as digital marketing campaigns, customer support operations, or product development projects.
Contract Administration Costs:
These costs cover the activities necessary to select and manage an outsourcing partner over the life of the contract. This includes legal fees, contract negotiation expenses, and ongoing management costs.
Transition Costs:
These are one-time costs associated with transitioning tasks from in-house to the outsourced provider. This can include training, setup fees, and any initial investments required to adapt systems or processes.
Avoided Costs:
Outsourcing often allows businesses to avoid direct and indirect costs associated with maintaining in-house operations. This includes salaries, benefits, equipment, office space, and training expenses for staff.
Potential Penalties or Additional Fees:
Some contracts may include penalties for non-compliance or additional fees for services beyond the initial scope.
To manage costs effectively while outsourcing, businesses should first evaluate their readiness and identify areas where outsourcing can yield significant savings without compromising quality. This involves analyzing current costs, selecting the right pricing model, and negotiating favorable terms with vendors. Implementing a comprehensive outsourcing plan includes setting clear expectations, maintaining open communication, and regularly reviewing performance metrics to ensure alignment with business objectives. Leveraging technology, such as AI and automation, can further streamline processes and reduce costs. Additionally, focusing on outsourcing non-core functions allows businesses to allocate resources more efficiently, leading to enhanced productivity and financial results. Continuous monitoring and evaluation of outsourced tasks are crucial for identifying areas of improvement and ensuring long-term cost savings.
The Impact Ofhsoring Has on Revenue and Business Growth
Outsourcing can drive revenue growth by improving operational agility, enhancing customer experience, and leveraging advanced technologies to stay competitive in the market.
Outsourcing can indirectly affect revenue by enhancing operations in several key areas:
Faster Time-to-Market: Outsourcing non-core functions allows businesses to focus on core activities, accelerating product development and launch cycles. This faster time-to-market enables companies to capitalize on emerging trends and customer needs more quickly, potentially increasing sales and revenue.
Better Customer Service: By outsourcing customer support to specialized providers, businesses can offer higher-quality, 24/7 service, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty. Satisfied customers are more likely to return and recommend the business, leading to increased revenue through repeat sales and positive word-of-mouth.
Access to Innovative Technologies: Outsourcing to providers with access to cutting-edge technologies can enhance operational efficiency and product quality. This access can lead to the development of innovative products or services that attract new customers and increase market share, ultimately boosting revenue.
When to Outsource and When Not To
By following this checklist, businesses can make informed decisions about whether outsourcing aligns with their strategic goals and operational needs:
Assess Business Readiness:
Understand Business Processes: Map out all processes to identify non-core functions.
Evaluate Financial Readiness: Assess costs and budget constraints.
Gauge Team Capacity: Ensure your team can manage an outsourcing partnership.
Ensure Legal Compliance: Familiarize yourself with outsourcing contracts and regulations.
Define Outsourcing Objectives:
Align with Business Goals: Ensure outsourcing supports strategic growth.
Identify Functions to Outsource: Focus on non-core activities.
Evaluate Potential Partners:
Expertise and Skills: Assess the partner’s specialized skills and experience.
Quality and Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Establish clear performance metrics.
Reputation and References: Research the partner’s track record.
Communication and Time Zones: Ensure effective communication channels.
Plan for Risk Management and Integration:
Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
Integration Plan: Define how outsourced functions will integrate with existing operations.
Establish Monitoring and Evaluation Systems:
Set Performance Metrics: Regularly review and adjust metrics as needed.
Continuous Feedback: Maintain open communication to address issues promptly.
There are, however, some scenarios in which outsourcing may not be the best business strategy. In these scenarios, maintaining in-house operations or exploring alternative strategies might be more beneficial to ensure quality, security, and compliance:
Core Competencies and Strategic Activities:
Outsourcing core functions or strategic activities can lead to a loss of control and expertise, potentially compromising competitive advantages. For instance, if a company’s core business is software development, outsourcing this function could dilute its expertise and innovation capabilities.
Highly Sensitive or Confidential Data:
When dealing with sensitive data, such as financial information or personal health records, outsourcing can increase the risk of data breaches and confidentiality issues. Ensuring strict security protocols is challenging, especially if the outsourcing partner’s security measures are not aligned with your standards.
Complex or Customized Processes:
Outsourcing complex or highly customized processes can be challenging due to difficulties in communication and ensuring that the outsourced provider fully understands the specific requirements. This can lead to quality control issues and delays.
High-Risk or High-Impact Projects:
For projects with significant financial or reputational risks, maintaining direct control and oversight is crucial. Outsourcing these projects can increase the likelihood of errors or failures, which might be difficult to rectify.
Cultural or Language Barriers:
When there are significant cultural or language barriers, outsourcing can lead to communication challenges, misunderstandings, and inconsistent service quality. This is particularly relevant in customer-facing roles where cultural alignment is important.
Regulatory Compliance:
In industries with strict regulatory requirements, outsourcing can complicate compliance efforts. Ensuring that external providers adhere to all relevant laws and regulations can be challenging and may lead to legal issues.

Steps to Implement an Effective Outsourcing Strategy
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to start outsourcing, from initial business analysis to final implementation:
Step 1: Assess Business Readiness
Assessing business readiness involves evaluating your organization’s internal capabilities, financial resources, and strategic goals to determine if outsourcing aligns with your business objectives and whether you have the necessary infrastructure to support an outsourcing partnership.
Define Outsourcing Goals: Clearly articulate your objectives, such as cost reduction, efficiency improvement, or skill acquisition.
Evaluate Internal Capabilities: Conduct an audit to identify gaps in current capabilities that outsourcing can fill.
Ensure Resource Availability: Confirm budget, staff, technology, and facilities to support outsourcing.
Gain Management Support: Engage key stakeholders early to secure their support.
Step 2: Define Project Scope and Resource Requirements
Defining project scope involves outlining the specific objectives, deliverables, and constraints of the outsourcing project, including defining features, functions, timelines, budgets, and necessary resources to ensure alignment with business goals and successful project execution.
Set Project Objectives: Outline specific goals and outcomes for the project.
Specify Features and User Experience Goals: Detail functionalities and user experience targets.
Plan System Integration: Consider how outsourced work will integrate with existing systems.
Establish a Timeline and Milestones: Set a clear timeline with key milestones.
Step 3: Choose a Reliable Outsourcing Partner
Choosing a reliable outsourcing partner involves selecting a suitable vendor by evaluating their expertise, track record, cultural fit, communication skills, and alignment with your project needs, ensuring they can deliver high-quality services and meet your business objectives.
Select a Suitable Region: Choose a region that fits your time zone, cultural compatibility, and budget preferences.
Evaluate Track Records and Feedback: Assess the provider’s history, client feedback, and case studies.
Conduct Thorough Interviews: Ensure methodologies and offerings align with project needs.
Assess Communication and Project Management: Evaluate communication protocols and project management tools.
Step 4: Establish Effective Communication Channels
Establishing effective communication involves setting up clear, consistent, and efficient communication protocols using tools like project management software and regular meetings to ensure seamless collaboration and timely issue resolution with the outsourcing partner.
Choose Communication Tools: Select tools like Slack, GitHub, and Zoom for efficient communication.
Set Regular Updates: Establish a schedule for regular updates and designate clear points of contact.
Step 5: Onboard and Train the Outsourced Team
Onboarding and training involve introducing the team to your company’s processes, tools, and project goals through comprehensive training sessions and practical demonstrations to ensure they are fully equipped to meet project requirements.
Host Onboarding Sessions: Introduce company tools, methodologies, and project goals to the outsourced team.
Provide Practical Demonstrations: Use practical demonstrations of project management tools.
Step 6: Ensure Clear Contracts and Agreements
Ensuring contracts involves drafting and finalizing comprehensive legal documents, such as service-level agreements and non-disclosure agreements, to protect intellectual property, define payment terms, and outline responsibilities and expectations for both parties.
Master Service Agreements (MSA): Outline project scope, payment terms, and confidentiality agreements.
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDA): Protect sensitive information shared during the project.
Intellectual Property (IP) Agreement: Define ownership of new IP created during the project.
Step 7: Monitor Progress
Monitoring involves regularly tracking the outsourcing project’s status through progress reports, performance metrics, and real-time data visualization tools to ensure timely completion, quality standards, and alignment with business objectives.
Request Progress Reports: Get regular updates from the outsourcing partner on completed tasks and upcoming milestones.
Use Dashboard Tools: Implement software for real-time data visualization to track progress and performance1.
Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Set KPIs to measure project success.
Step 8: Implement and Manage the Outsourcing Process
Implementing involves transitioning tasks to the outsourcing partner, ensuring seamless integration with existing operations, and maintaining ongoing management through regular communication, performance monitoring, and continuous improvement to meet business objectives.
Project Initiation and Transitioning: Begin the outsourcing project and transition tasks smoothly.
Managing Service Delivery: Continuously manage and improve service quality.
Step 9: Plan for Exit Strategy
Planning for exit strategy involves developing a comprehensive exit plan that outlines objectives, identifies alternative solutions, assigns roles and responsibilities, defines success criteria, and establishes indicators to monitor the outsourcing arrangement, ensuring a smooth transition of services in case of contract termination or expiration.
Outline Termination Protocols: Develop protocols for smoothly ending the outsourcing contract.
Plan for Dispute Resolution: Establish steps to address potential disputes.
Step 10: Review and Adjust
Reviewing and adjusting involves conducting regular evaluations of the outsourcing arrangement to assess its effectiveness, gather feedback from stakeholders, and make necessary adjustments to the strategy, processes, or partnerships to ensure ongoing alignment with business goals and optimal performance.
Conduct Regular Reviews: Assess the effectiveness of the outsourcing plan and make adjustments as needed.
Adjust Strategy Based on Feedback: Use feedback from stakeholders and the outsourcing partner to refine the strategy.
Interested in Learning How Offshoring Can Help Your Business?
Outsourcing can significantly impact business profitability and quality by allowing companies to leverage skills and economies of scale, thereby reducing operational costs and enhancing profitability. It also enables businesses to focus on core operations, driving strategic growth and innovation. Access to advanced technologies and expertise can improve product or service quality, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. However, effective outsourcing requires careful planning and management, including assessing business readiness, defining project scope, selecting reliable partners, establishing clear communication channels, and continuously monitoring performance. By adopting a structured approach to outsourcing and managing associated risks, businesses can ensure successful outcomes that align with their strategic objectives, ultimately improving both profitability and quality.
Does outsourcing align with your strategic goals? Schedule a talk with a recruiting specialist to find out how Go Carpathian can help you improve work quality while reducing hiring costs!



